Network Topology
There are 5 types of network topologies:
- Bus topology
- Star topology
- Ring topology
- Mesh topology - (most common)
- Tree topology - (least common)
| Topology | Diagram | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bus | 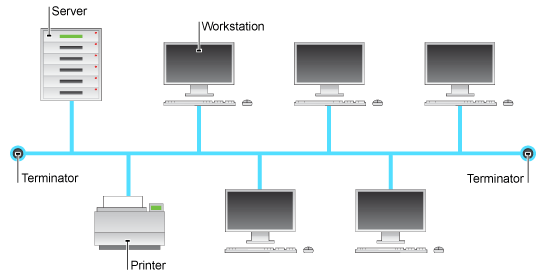 |
|
|
| Star | 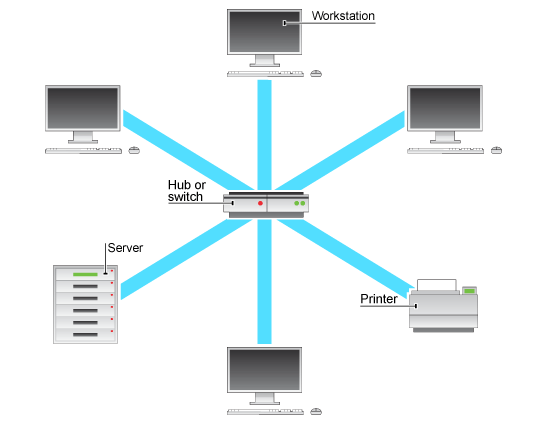 |
|
|
| Ring | 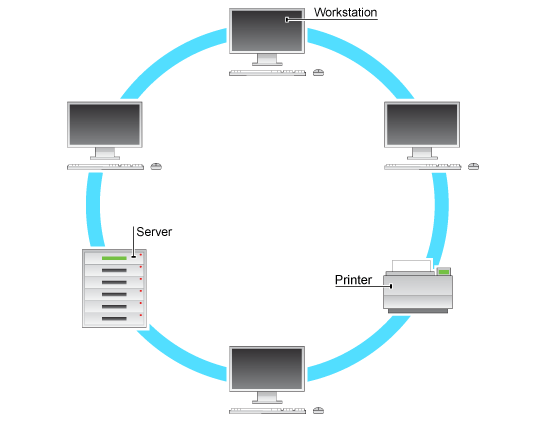 |
|
|
| Mesh | 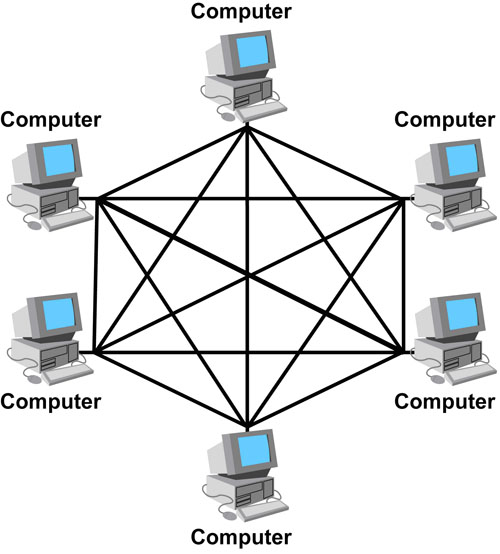 |
|
|
| Tree | 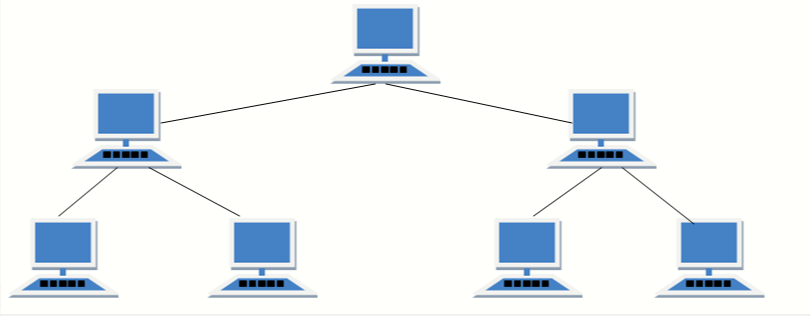 |
|
|